Top Cybersecurity Standards for Financial Institutions: A Complete Guide
Share

In today’s hyper-connected financial ecosystem, cybersecurity isn’t just a regulatory requirement, it’s a critical pillar of trust and business continuity. Financial institutions handle vast volumes of sensitive customer data and high-value transactions daily, making them prime targets for cybercriminals. To protect their operations and maintain customer confidence, banks, fintech companies, and other financial organizations must adopt robust cybersecurity standards.
This guide explores the top cybersecurity standards for financial institutions, explains why they matter, and highlights real-world applications that demonstrate their effectiveness.
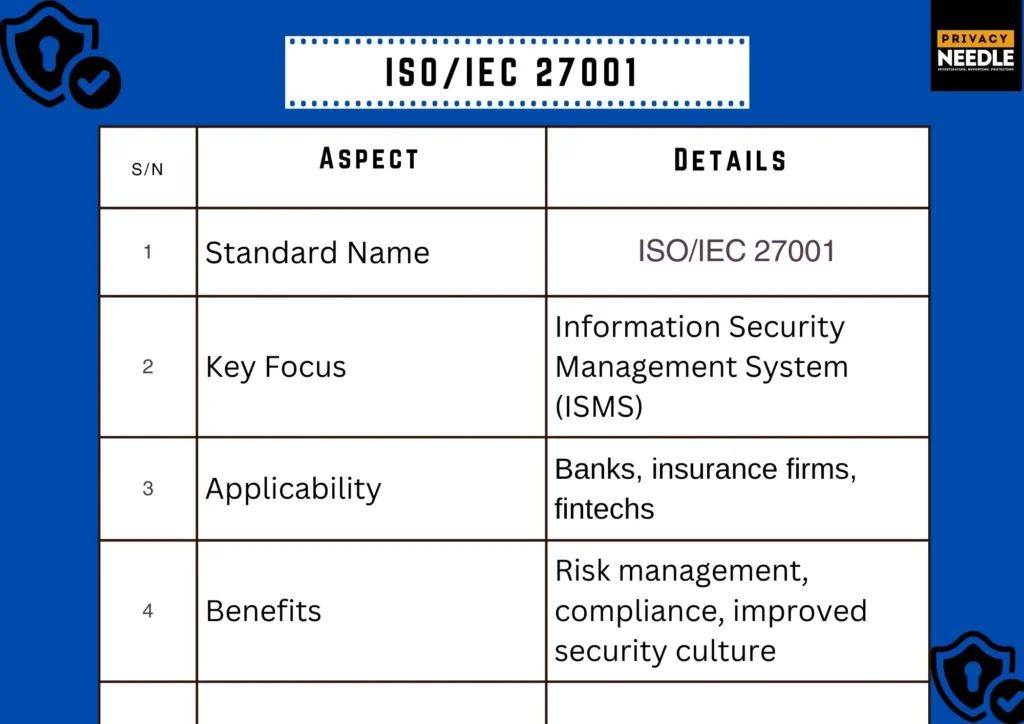
1) ISO/IEC 27001: The Global Benchmark for Information Security
ISO/IEC 27001 is an internationally recognized standard for information security management systems (ISMS). It provides a structured framework for managing sensitive information, ensuring its confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
Key Features:
- Risk-based approach to information security
- Comprehensive ISMS implementation
- Regular audits and continuous improvement
Why It Matters for Financial Institutions: Financial institutions deal with massive amounts of sensitive data, from personal banking information to transaction records. ISO 27001 helps organizations systematically manage risks and ensure compliance with both local and international regulations.
Real-Life Example: HSBC adopted ISO/IEC 27001 to strengthen its global security posture. By standardizing its security controls across different jurisdictions, the bank improved regulatory compliance and reduced security incidents by 25% within the first year.
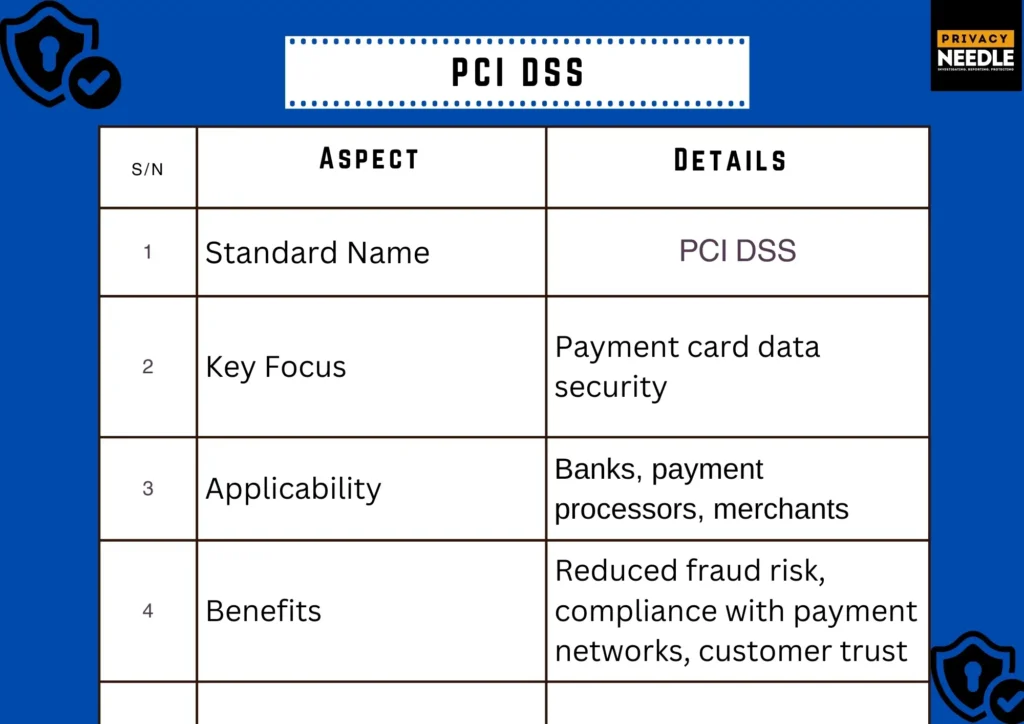
2) PCI DSS: Protecting Payment Card Data
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is mandatory for any organization that stores, processes, or transmits cardholder data. It was developed by major credit card companies to prevent payment fraud and data breaches.
Key Features:
- Strong access control measures
- Regular network monitoring and testing
- Secure storage and transmission of cardholder data
Why It Matters: Financial institutions that handle credit and debit card transactions must comply with PCI DSS to avoid fines, legal liabilities, and reputational damage.
Real-Life Example: In 2020, a mid-sized U.S. credit union avoided a potential $2 million breach by implementing tokenization and encryption as part of its PCI DSS compliance strategy. This proactive approach helped protect customer data even during an attempted cyberattack.
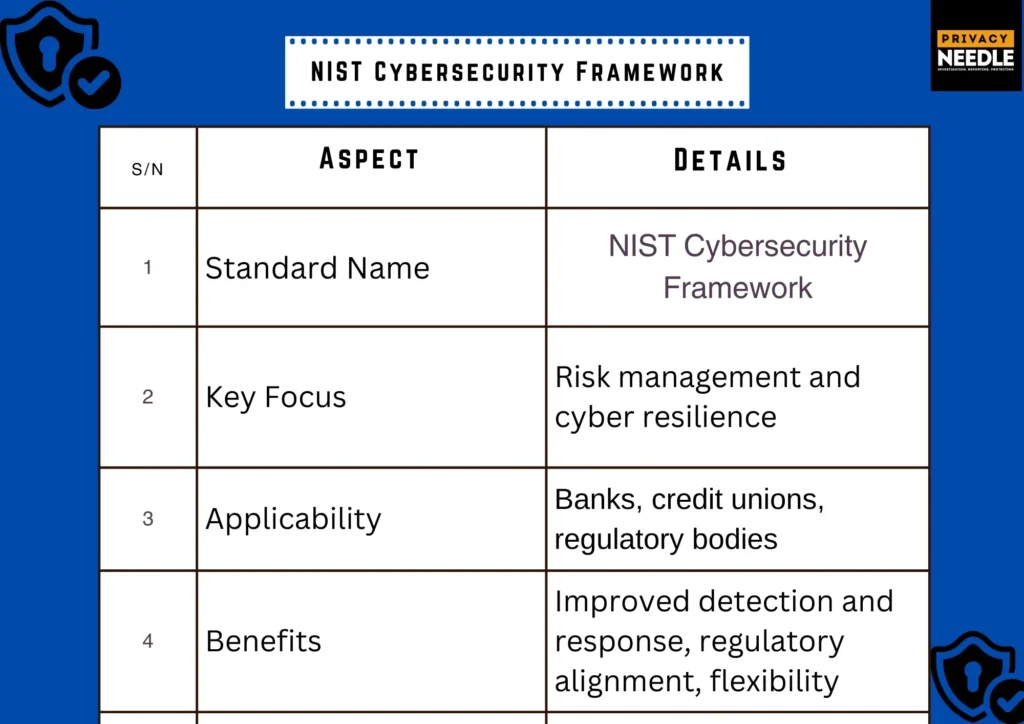
3) NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) : U.S. Standard with Global Influence
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) CSF provides a voluntary but widely adopted framework for managing and reducing cybersecurity risks. It is built around five core functions: Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover.
Key Features:
- Flexible and adaptable to different organizational needs
- Emphasizes continuous monitoring and improvement
- Integrates well with other regulatory requirements
Why It Matters: Many central banks and regulatory authorities encourage or require financial institutions to align with NIST CSF due to its comprehensive nature and adaptability.
Real-Life Example: The Federal Reserve Bank of New York used NIST CSF to strengthen its cyber resilience strategy. As a result, it improved incident response times by 40% and enhanced collaboration between security teams and business units.
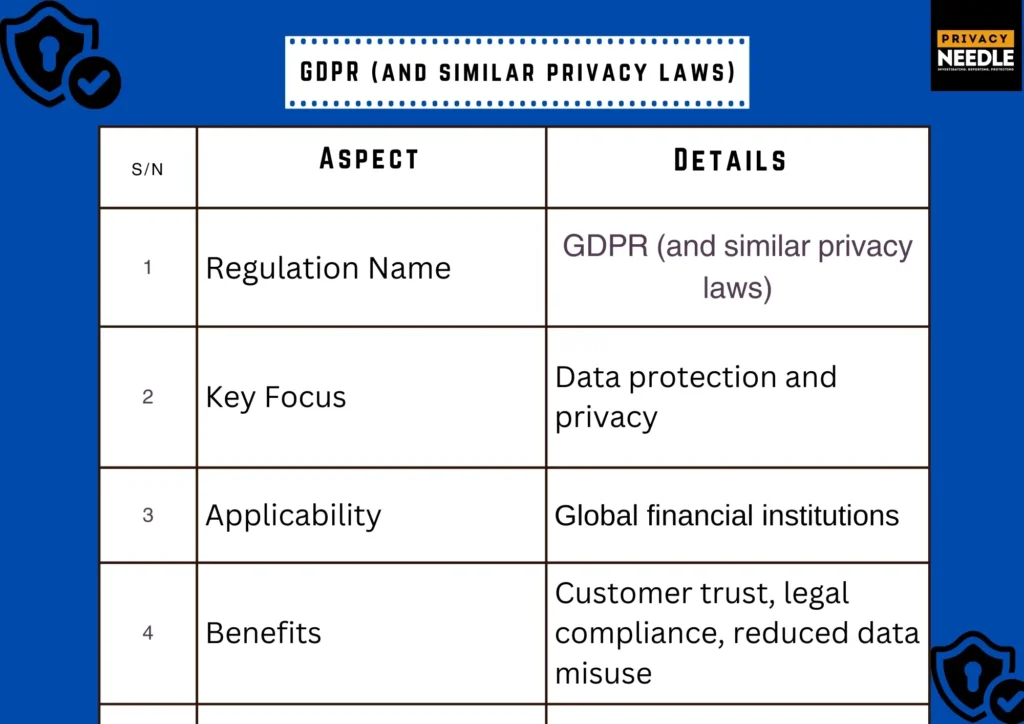
4) GDPR & Data Privacy Regulations: Protecting Customer Trust
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), though European, has global implications for any financial institution processing the data of EU citizens. GDPR sets strict rules for data collection, storage, and processing, emphasizing individual privacy rights.
Key Features:
- Data minimization and purpose limitation
- Mandatory data breach notifications
- Heavy penalties for non-compliance (up to 4% of global turnover)
Why It Matters: Financial institutions often operate globally and must comply with GDPR alongside local privacy laws such as Nigeria’s NDPR or California’s CCPA. Compliance builds trust and prevents costly legal issues.
Real-Life Example: In 2021, a leading European bank was fined €4.5 million for failing to properly anonymize customer data. This highlighted the importance of GDPR compliance for reputation and legal safety.
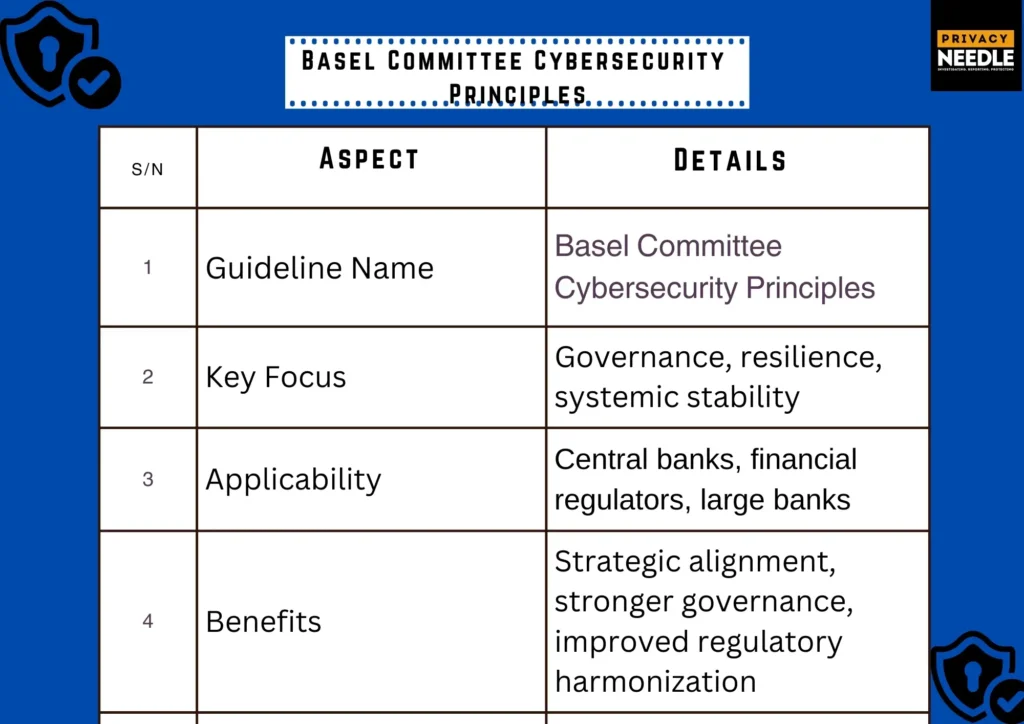
5) Basel Committee Cybersecurity Principles: Guiding Global Financial Stability
The Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS) has issued cybersecurity principles that focus on governance, risk assessment, monitoring, and incident response. While not a strict standard like ISO, these principles influence global banking regulations.
Key Features:
- Strong board and senior management oversight
- Clear cyber risk appetite and strategy
- Integration of cybersecurity into enterprise risk management
Why It Matters: Basel principles provide high-level guidance that regulators use to shape their own cybersecurity requirements for financial institutions. They emphasize resilience and systemic stability.
Real-Life Example: Several Asian central banks adopted Basel’s principles to harmonize their cybersecurity regulations, leading to improved cross-border cooperation and incident reporting among financial institutions.
FAQs: Cybersecurity Standards for Financial Institutions
Q1: Are cybersecurity standards legally binding for financial institutions?
Not all standards are legally binding. Some, like PCI DSS and GDPR, have mandatory compliance elements. Others, like NIST CSF and Basel principles, are voluntary but widely adopted to meet regulatory expectations and improve resilience.
Q2: How often should financial institutions update their cybersecurity controls?
Regular updates are crucial. Most standards recommend annual reviews, but in practice, continuous monitoring and quarterly updates are ideal, given the fast-evolving threat landscape.
Q3: What happens if a bank fails to comply with cybersecurity regulations?
Non-compliance can result in fines, legal action, reputational damage, and even operational restrictions. For example, GDPR violations can lead to penalties of up to 4% of annual global turnover.
Q4: Which standard should a small fintech company prioritize first?
For startups and small fintechs, PCI DSS (if handling payments) and ISO/IEC 27001 provide the strongest foundational security frameworks. NIST CSF can then be layered for more mature risk management.
Final Thoughts
Cybersecurity standards are not just boxes to check, they’re strategic tools that help financial institutions build trust, resilience, and competitive advantage. By implementing globally recognized frameworks such as ISO/IEC 27001, PCI DSS, NIST CSF, GDPR, and Basel Principles, organizations can protect their assets, safeguard customer data, and stay ahead of regulatory requirements.
In a rapidly evolving digital landscape, adopting these standards is not optional, it’s essential for survival and growth.





































Leave a Reply